Projects
dxgfsd
sssssssssssss
tze
qqqqqqqqqqqq
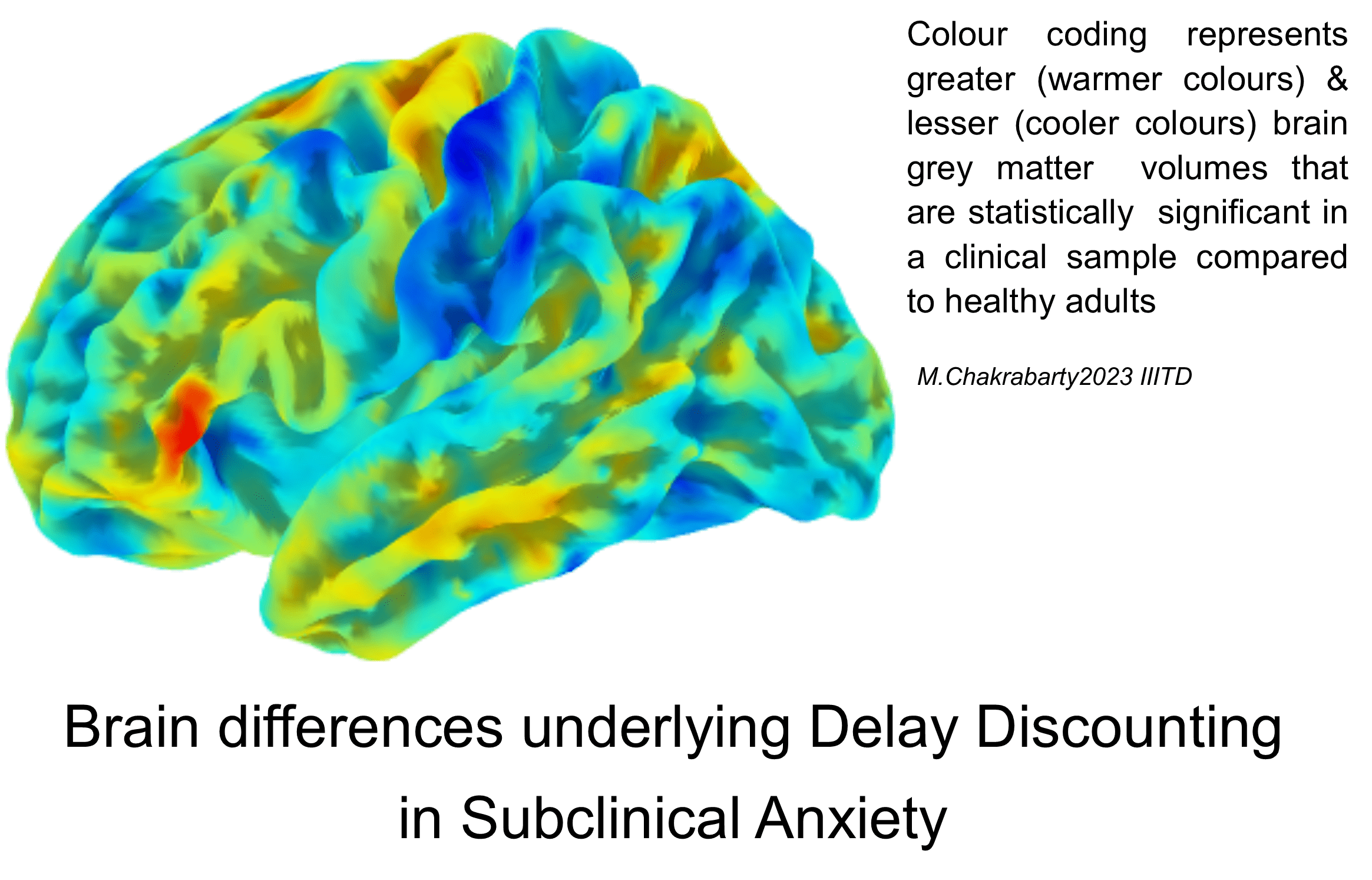
Brain Differences Underlying Delay Discounting in Subclinical Anxiety
An understanding of the embedded cognitive processes implemented by the brain that elucidate the brain-behaviour dimension is fundamental to arriving at better (clinical) approaches to diagnoses and interventions of mental health disorders. Along this line, objective measures of specific behaviour/cognitive function and brain are of merit in arriving at accurate descriptions of individuals/patients for suitable intervention(s). Towards this end, this project seeks to investigate the potential merit of the quantitative behaviour and brain-based measures from the cognitive phenomenon of ‘delay discounting of future rewards’, to index the individual severity of anxiety.

AI Empowered Attention Evaluation among Children with ADHD
Specific Learning Disabilities (SLDs) conditions manifest as a deficit in processing language, spoken or written, that may manifest itself as a difficulty to comprehend, speak, read, write, spell, or to do mathematical calculations and includes such conditions as perceptual disabilities, dyslexia, dysgraphia, dyscalculia, dyspraxia, and developmental aphasia. The cognitive flexibility associated with SLDs can manifest itself in noteworthy talents, which include a multi-sensory lens for creative and lateral thinking, resulting in out-of-the-box solutions for problems. The untapped potential of SLDs causes a high opportunity cost for the Nation's progress. However, children with SLDs experience repeated failures and poor performance despite their continuous efforts and practice in learning. At the same time, worldwide, the condition will SLDs has been exacerbated due to the COVID-19 pandemic when education delivery shifted online. Thus, strengthening online education delivery will be important and impacting. However, research has indicated that educators might not always be aware of their student's attentional focus, and this may be particularly true for novice teachers. The aim of this project is to develop an AI-empowered tool that will offer personalized, monitored, and evidence-based identification of attention levels among children with SLD. The project will first develop a multimodal dataset of audio-visual and physiological signals among 150 children with SLD to understand the attention and engagement of children with SLD during digital learning. It will further perform a systematic comparison of physiological, audio-visual, and eye-dilation signals for the attention monitoring of children with SLD to identify the valid indicators of attention. Based on these, the project will develop an AI-empowered system for real-time continuous monitoring of attention among children with SLD. Finally, the project will deploy and evaluate the efficacy of the developed AI-empowered system among 50 children with SLD and 25 typically developing children in naturalistic settings. Once validated the findings of this project can improve and monitor the attention of children with SLDs and can play a significant role in their inclusion during digital learning.
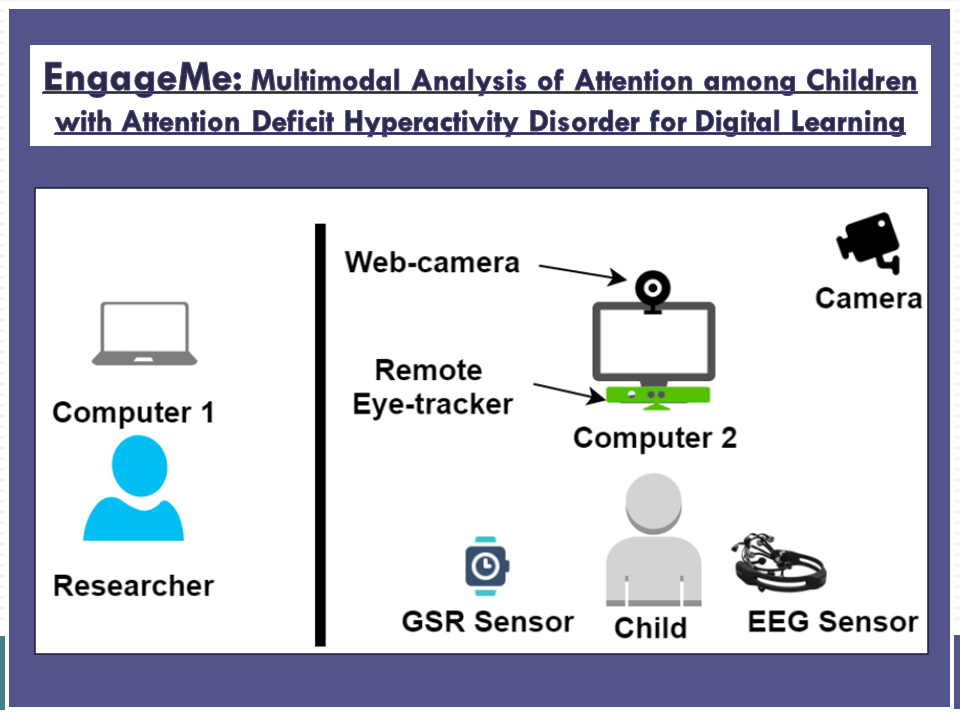
EngageMe: Multimodal Analysis of Attention among Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder for Digital Learning
Children with Specific Learning Disabilities (SLDs) experience repeated failures and poor performance despite their continuous efforts and practice in learning. At the same time, worldwide, the condition with SLDs has been exacerbated due to the COVID-19 pandemic when education delivery shifted online. Thus, strengthening online education delivery will be important and impacting. However, research has indicated that educators might not always be aware of their student's attentional focus, and this may be particularly true for novice teachers. The aim of this project is to develop an AI-empowered tool that will offer personalized, monitored and evidence-based identification of attention level among children with SLD. Once validated, the findings of this project can improve and monitor the attention of children with SLDs and can play a significant role in their inclusion during digital learning.
Exploring the Design of XR Enabled Accessible Learning Experiences
XR has widely been used for creating engaging user experiences, gaming, and education. However, its application for creating accessible and engaging learning experiences for persons with sensory impairments has not been widely explored. This proposed project will explore the design of engaging and accessible learning experiences for persons with special needs.

Harnessing AI and Multimodal Data for Social Good
In recent years, advances in artificial intelligence techniques have yielded immense success in computer vision, natural language processing, and speech processing. Healthcare is also one of the areas which got many benefits from this. Mining social media messages for health and drug-related information has received significant interest in pharmacovigilance research. For instance, an analysis of social media text (e.g., tweets, posts, and comments) using natural language processing and machine learning techniques helps in finding the adverse drug reactions, suicidal ideation, depression detection, medical information extraction, etc. Moreover, computer vision and machine learning techniques help the automatic detection of different diseases from tissue images. For instance, it has shown immense success in the detection of cancer, diabetes, kidney failure, etc. Furthermore, speech processing in conjunction with artificial intelligence has shown great success in the treatment of people. Moreover, artificial intelligence helps in building systems for people with different abilities. At MIDAS@IIITD, we focus on several such interesting research problems (e.g., kidney glomeruli classification, automatic kidney fibrosis assessment, adverse drug reactions, and suicidal ideation ) leveraging deep learning techniques. Our recent papers in this area are published in top-tier conferences and journals such as IEEE Intelligent Systems, NAACL, etc.

Improving Mental Health Through Continuous Objective Measurement and Personalized Intervention
Under stress, we experience an increased heart rate, reduced Heart Rate Variability (HRV), and excessive sweating, leading to an increase in skin conductance. Hence these physiological signals can be used as a biomarker to identify stress in an individual. EDA indicates the emotional arousal of a person by measuring skin conductivity, while HRV captures variation in time elapsed between successive heartbeats. PPG is used to understand the activity of the heart by measuring blood flow. PPG signals can be used to calculate HRV. However, studies have shown that EDA is a motion-sensitive signal, even the process of digestion and increased sweating at high temperatures and humidity can change the EDA measurements [2]. Moreover, skin conductivity also increases during sleep. Hence, EDA alone might not give reliable predictions, and we rely on both EDA and HRV to predict stress.

Pupillometry using Smartphones
Developing economies have paved the way for technology to reach out to even the remotest of places and people from all walks of life; a testament to that is the affordability of smartphones. We want to propose a smartphone application that will help in early-level diagnosis or measure the propensity of neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental disorders by measuring the pupil dynamics of the eye captured from the in-built camera.
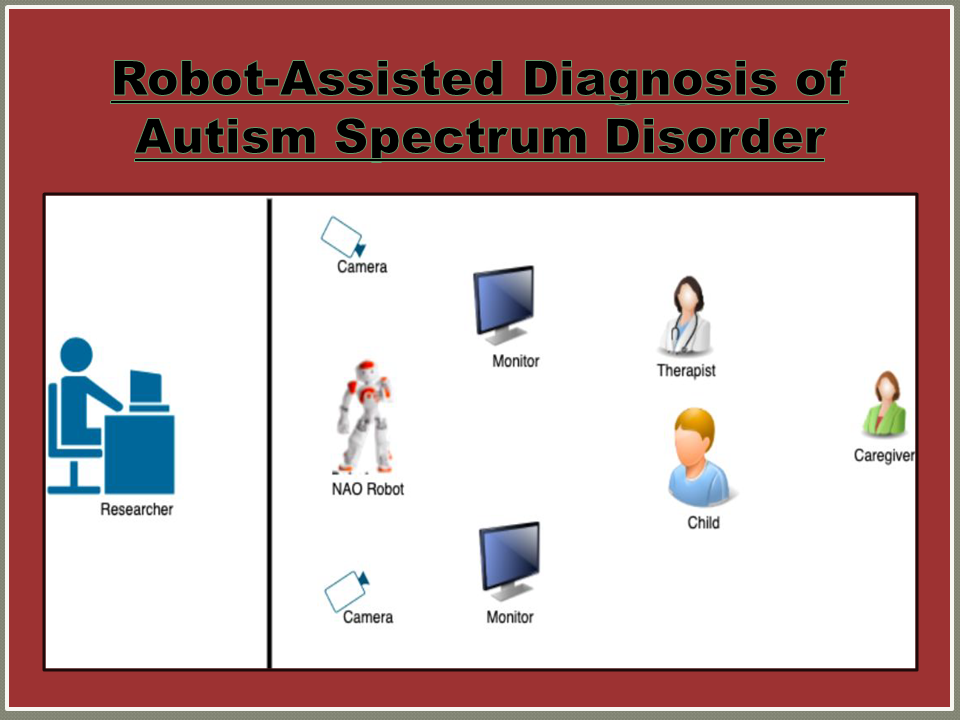
Robot-Assisted Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
Early detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is crucial for deciding the appropriate educational and behavioral intervention at the most suitable time. However, there are no absolute biological markers for autism and accurate diagnosis of ASD requires extensive training and experience acquired over the years and such expertise is limited to a few individuals centered in metropolitans and is beyond the reach of most of the affected population. robot-assisted interventions have found increasing acceptance as a support tool for therapy and education for children with autism (CwA). CwA prefers to interact with technological tools rather than human beings and hence, robot-assisted diagnosis systems can be employed to improve the early detection of ASD in an automated assessment manner making the ASD diagnosis more objective. The overarching goal of this project is to develop a robot-assisted system for the diagnosis of ASD suitable to children of Indian ethnicity. Upon validation, the benefits of this project can be made available to the unreachable children masses of India.

Smart Camera for Enforcing Social Distancing and Face Mask Detection
We propose to develop a plug-and-play extension for existing CCTV cameras in public places for enforcing social distancing and face mask detection. The solution incorporates computer vision techniques and uses the frame-by-frame information of CCTV to detect people and classify violations of social distancing norms. The solution will also perform real-time face mask detection. The techniques will be robust and can perform without any calibration and will be capable of detecting varying geometries of face masks and perform under degrees of natural illumination. In case of a detected violation, a voice alert can be issued. Further, the timestamp of violation with the snapshot of the frame highlighting the associated subjects will be sent to a central database and emailed to the authorities for further action.

Studying the Role of Human Movement in the Metaverse
We propose to study from an applied perspective the role of human movement in the Metaverse. Firstly, we would synthesize and analyze the existing approaches to body movement detection. Secondly, the study would involve building prototypes of social, work, or play experiences using contemporary methods of motion detection. Thirdly, we would draw out the guidelines a designer must follow when designing with a specific implementation technique in mind. Lastly, we would come up with recommendations for tools and APIs to be built to democratize the use of human motion in Metaverse experiences. We believe that through this effort we will be able to push the boundary of the applicable knowledge and consideration for human body movement as an interaction mechanism.

Understanding Digital Technology use for Well-Being for LGBTQIA+ University Students in India
In this work, we intend to explore the digital technology use amongst LGBTQ+ adults in India. We sought to understand the experiences of LGBTQ+ adults using digital technologies such as social media, dating applications, the Internet, etc. in their day-to-day lives. Through this work, we would like to contribute toward a cross-cultural understanding of queer people's use of digital technology with respect to social issues.

VERTIGLOBAL: A Global Telehealth Solution for VERTIGO
The expected outcomes of the proposed study are: 1. Designing and building of low-cost, easy-to-use, portable, robust, and effective device for nystagmus eye tracking 2. Building mobile application/web portal for generating different reports automatically based on nystagmus eye tracking 3. Building machine learning models to automatically perform vHIT in vertigo diagnosis

Towards Accessible and Inclusive Artificial Intelligence (AIAI): Building on Finnish and Indian Expertise, Experiences, and Diversity
A consortium of experts and professional working technology for the digital transformation of society with a focus on marginalized and vulnerable communities and user groups, on topics of Accessibility, Inclusion, and innovative technologies such as AI.
sdfsdf
qqqqqq
